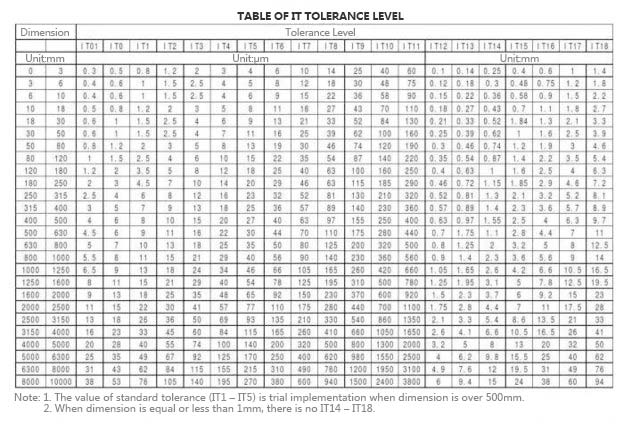
Machining accuracy is mainly used to characterize the fineness of the manufactured product and is a term used to evaluate the geometric parameters of the machined surface. Machining accuracy is measured by tolerance class. The smaller the grade value is, the higher the precision is.
There are 20 tolerance levels from IT01, IT0, IT1, IT2, IT3 to IT18. IT01 indicates that the machining accuracy of the part is the highest. IT18 indicates that the machining accuracy of the part is the lowest. The general mining machinery belongs to IT7, and the general agricultural machinery belongs to IT8 level. According to the different functions of the product parts, the machining precision that need to be achieved is different, and the selected processing forms and processing techniques are also different. This paper introduces the machining accuracy that can be achieved by several common machining forms such as turning, milling, planing, grinding, drilling and boring.
The workpiece rotates and the turning tool performs a straight or curved movement in the plane. Turning is usually carried out on a lathe to machine the inner and outer cylindrical faces, end faces, conical faces, forming faces and threads of the workpiece.
The turning precision is generally IT8-IT7, and the surface roughness is 1.6-0.8μm.
1) Rough turning seeks to improve turning efficiency with large cutting depth and feed without reducing cutting speed, but the machining accuracy can only be up to IT11, surface roughness of Rα20—10μm.
2) Semi finish turning and finish turning try to use high speed and small feed and cutting depth, machining accuracy up to IT10 -- IT7, surface roughness Rα10—0.16μm.
3) Finish turning of non-ferrous metal parts on high precision lathes with finely honed diamond turning tools at high speed enables the machining accuracy to reach IT7 -- IT5 with surface roughness of Rα0.04—0.01μm. This type of turning is called "mirror turning".
Milling refers to the use of a rotating multi-blade tool to cut a workpiece, which is a highly efficient machining method. Suitable for processing planes, grooves, various forming surfaces (such as splines, gears and threads) and special shapes of the mold. According to the same or opposite direction of the main moving speed direction and the workpiece feeding direction during milling, it is divided into down milling and up milling.
The machining accuracy of milling is generally up to IT8-IT7, and the surface roughness is 6.3-1.6μm.
1) Machining accuracy during rough milling IT11—IT13, surface roughness 5-20μm.
2) Machining accuracy during semi-finish milling IT8—IT11, surface roughness 2.5-10μm.
3) Machining accuracy during finish milling IT16-IT8, surface roughness 0.63-5μm.
Planing is a cutting method that uses a planer to horizontally reciprocate the workpiece horizontally. It is mainly used for the shape processing of parts.
The machining accuracy of planing is generally up to IT9-IT7, and the surface roughness is Ra6.3-1.6μm.
1) Machining accuracy of rough planing can reach IT12-IT11, and the surface roughness is 25-12.5μm.
2) Machining accuracy of semi-finish planing can reach IT10-IT9, and the surface roughness is 6.2-3.2μm.
3) Machining accuracy of finish planing can reach IT8-IT7, and the surface roughness is 3.2-1.6μm.
Grinding refers to the processing method of using abrasives and abrasive tools to remove excess materials on the workpiece. It belongs to the finishing industry and is widely used in the machinery manufacturing industry.
Grinding is usually used for semi-finishing and finishing, with an accuracy of IT8-IT5 or higher, and surface roughness is generally 1.25-0.16μm.
1) Precision grinding surface roughness is 0.16-0.04μm.
2) Ultra-precision grinding surface roughness is 0.04-0.01μm.
3) The surface roughness of mirror grinding can be less than 0.01μm.
Drilling is a basic method of hole machining. Drilling is often carried out on drill presses and lathes, or on a boring machine or milling machine.
Drilling has a low processing precision, generally only achieves IT10, and the surface roughness is generally 12.5-6.3μm. After drilling, reaming and reaming are often used for semi-finishing and finishing.
Boring is an internal diameter cutting process that uses tools to enlarge holes or other circular contours. Applications range from semi-roughing to finishing. The tools used are usually single-edged boring tools (called boring bars).
1) The precision of the boring of steel materials is generally up to IT9-IT7, and the surface roughness is 2.5-0.16μm.
2) The precision of precision boring can reach IT7-IT6, and the surface roughness is 0.63-0.08μm.
The following table is more intuitive.